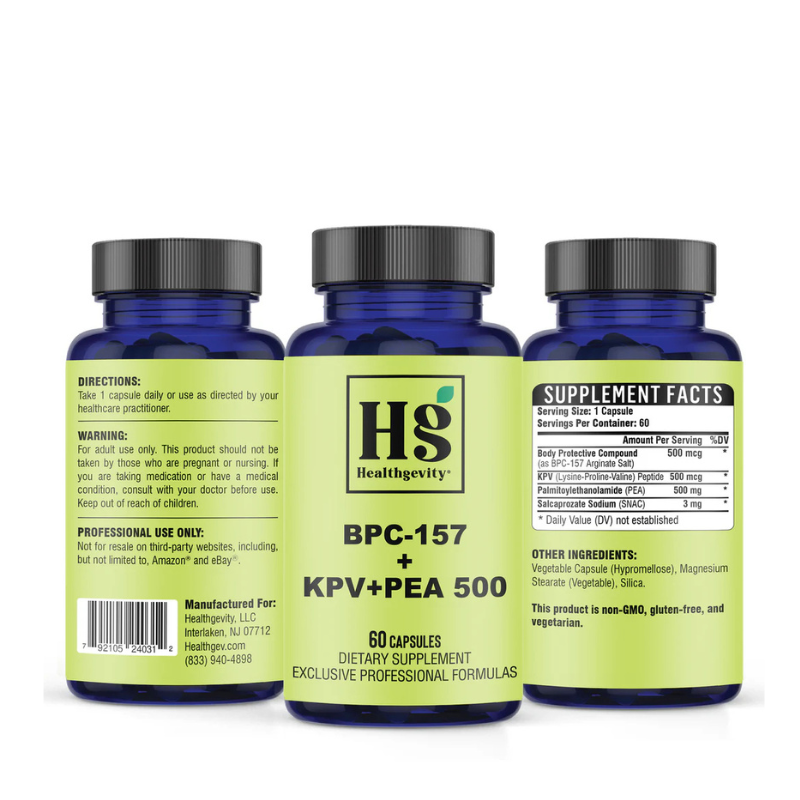
BPC-157 + KPV + PEA 500
BPC-157 + KPV + PEA 500
Couldn't load pickup availability
BPC-157 + KPV + PEA 500 – Advanced Support for Inflammation and Gut Health
Enhance your body's natural healing processes with BPC-157 + KPV + PEA 500, a synergistic blend formulated to support inflammation management, tissue repair, and overall gut health. This advanced supplement combines BPC-157, KPV (Lysine-Proline-Valine), and Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), enhanced with salcaprozate sodium (SNAC) for superior absorption.
Key Benefits:
-
Inflammation Support: BPC-157 and KPV are peptides known for their anti-inflammatory properties, aiding in the reduction of inflammation throughout the body.
-
Tissue Repair and Regeneration: BPC-157 promotes healing of tissues, supporting recovery from injuries and enhancing overall tissue health.
-
Gut Health Enhancement: KPV and PEA contribute to maintaining a healthy gut lining, supporting digestive health and integrity.
-
Enhanced Absorption: The inclusion of SNAC ensures optimal bioavailability of the active ingredients, maximizing their efficacy.
Premium Ingredients:
-
BPC-157: A pentadecapeptide derived from human gastric juice, known for its role in promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation.
-
KPV (Lysine-Proline-Valine): A tripeptide with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, supporting immune function and gut health.
-
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA): An endocannabinoid-like lipid mediator with documented anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and neuroprotective effects.
-
Salcaprozate Sodium (SNAC): An absorption enhancer that improves the bioavailability of peptides and other compounds.
Pure Quality You Can Trust:
-
Non-GMO and Gluten-Free: Suitable for individuals with dietary sensitivities.
-
No Artificial Additives: Free from unnecessary fillers, binders, and artificial ingredients.
-
Manufactured in GMP-Certified Facilities: Ensures high-quality production standards and product consistency.
Why Choose BPC-157 + KPV + PEA 500?
This formulation offers a comprehensive approach to managing inflammation and supporting tissue repair. The combination of BPC-157, KPV, and PEA, enhanced with SNAC for superior absorption, ensures that your body receives the support it needs for optimal healing and health.
Support your body's healing processes with BPC-157 + KPV + PEA 500 today!
Important: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Always consult with your physician or healthcare provider before starting any new dietary supplement, especially if you have a medical condition or are taking other medications.
Share